Having completed two phases of its vaccination drive, India now gears on towards the third. Starting May 1st, all citizens above the age of 18 are eligible to take their jab against COVID-19. If you plan on getting your dosage, here’s what you’ll need to know!
Essential Information
- The registration process for the vaccine will begin on the 28th of April. All citizens above 18 years of age can register to receive the vaccine.
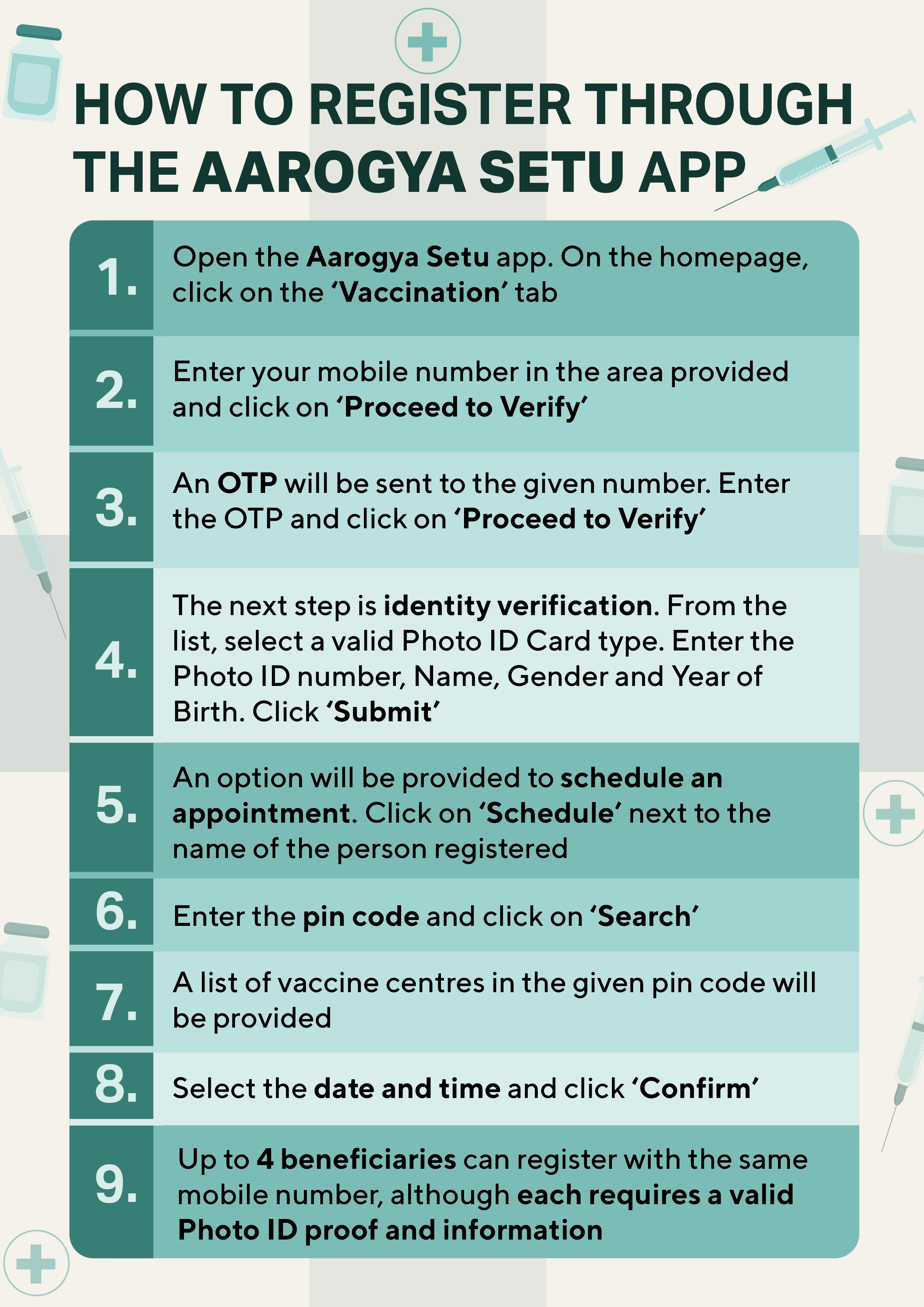
- Registration must be done through the CoWin portal or the Aarogya Setu app. No walk-in appointments are permitted at the Covid Vaccination Centres (CVCs).
- A valid government-approved photo ID is the only required document that must be presented both at the time of registration and on the day of vaccination.
- Following the online registration, the beneficiary will be notified of their vaccination schedule via SMS.
- At present, Covishield and Covaxin are being administered to beneficiaries in India. There is no head-to-head comparison of the two based on their effectiveness. Both vaccines have proved to significantly reduce the requirement for hospitalisation and the severity of the infection. Hence, you may receive any of them.
- Covishield is currently priced at Rs 400 to Rs 600 per dose. Covaxin is available at Rs 600 in state hospitals and Rs 1200 in private hospitals for each shot.
- You must receive the same vaccine in both doses as the compatibility of different COVID vaccines has not been studied yet.
Currently, India has three vaccines lined for distribution—Covishield, Covaxin and Sputnik V. Read on to get a quick idea of their basics.
COVISHIELD
Baseline
Covishield, developed by Oxford University and Swedish-British pharma major AstraZeneca, is the first coronavirus vaccine to receive a regulatory nod in India. It is being manufactured in the Pune facility of the Serum Institute of India (SII).
How does the vaccine work?
The Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine or Covishield (ChAdOx1) uses an adenovirus approach. The vaccine is essentially based on a weakened version of a common cold virus found in chimpanzees. Interestingly, this viral vector contains the genetic material similar to coronavirus’ spike protein. Being an inactivated vaccine, it is modified to look like SARS-CoV-2 and alerts our immune systems to create antibodies.
Shelf-life/Storage conditions
Shelf life: six months
Storage: 2 to 8 degree Celsius
Dosage
Interval between first and second dose: 4-6 weeks
Efficacy
The World Health Organization sets the overall effectiveness of the Covishield vaccine to be 63 per cent. International clinical trials of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine showed that if the vaccine is administered in half a dose and then a full dose after a month, the efficacy rate is around 90 per cent. However, the data surrounding this idea is still unclear. Currently, in India, the overall effectiveness of the vaccine is 70 per cent.
Issues developed post-vaccination
According to the fact sheet for a Covishield vaccine recipient, people experience the following mild-to-moderate side effects post-inoculation. However, this varies from person to person. You may or may not experience these, and it’s nothing to worry about either way:
Very common-
Tenderness, pain, numbness and redness where the injection is given.
Tiredness and fatigue
Feeling feverish
Headache
Joint pain or muscle ache
Nausea
Common-
A lump at the injection site
Fever
Vomiting
Flu-like symptoms (high temperature, sore throat, runny nose, cough, chills)
Uncommon-
Dizziness
Decrease in appetite
Abdominal pain
Excessive rashes
COVAXIN
Baseline
Covaxin, India’s first indigenous vaccine, has been developed by Bharat Biotech in collaboration with the Indian Council of Medical Research. It is being manufactured in Bharat Biotech’s high bio-containment facility.
How does the vaccine work?
The vaccine contains six micrograms of inactivated or dead SARS-CoV-2 antigen that prompts an immune response in the vaccinated individual. This leads to the production of antibodies, leading to immunity against live coronaviruses.
Shelf-life/Storage Conditions
Shelf life: nine months
Storage: 2 to 8 degree Celsius
Dosage
Interval between first and second dose: 4-6 weeks
Efficacy
In the ongoing phase III clinical trial conducted with 25,800 subjects, the vaccine’s interim efficacy is estimated at 81%. Studies show that the vaccine is effective against the UK variant of SARS-CoV-2. It is unclear how many months of immunity the vaccine provides. It is possible that the number of antibodies may reduce; however, if the immune system’s memory B cells retain information, they can create antibodies against coronavirus for years.
Issues developed post-vaccination
Covaxin has been approved for restricted usage in the current emergency for those of age 18 and older; however, the effects of the vaccine on certain groups of individuals have not been studied yet. In some cases, Covaxin can cause a severe allergic reaction. Individuals with allergies to any of the vaccine’s ingredients or those who have experienced an allergic reaction to the first dose must not be vaccinated.
A few side effects of Covaxin have been reported; however, the immune response varies in each individual. You may experience some flu-like symptoms that generally subside within two days. The most commonly reported side effects are:
- Pain at the injection site
- Headache, fever, body ache
- Sweating, cold, cough
SPUTNIK V
Baseline
Sputnik V is a viral vector vaccine for COVID-19. Developed by the Gamaleya Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology, Sputnik V is the world’s first registered vaccine. Its Phase I and Phase II clinical trials took place in August 2020.
How does it work?
Similar to Covishield, with SputnikV, a gene with similarities to the coronavirus spike protein is inserted into an adenoviral vector during creation. Adenoviral vectors are non-enveloped double-stranded DNA vectors. A vector is essentially a virus, but its gene for mutation is removed. Thus, it no longer possesses a threat to the body and cannot cause an infection. This is recognised by our immune system, and thus, the body starts to produce antibodies that can fight the virus.
Dosage
Unlike most adenovirus viral vector vaccines, Sputnik V has a slightly different approach to dosage. It is a two dosage vaccine, but Sputnik V uses a different neutralised vector for each jab, and the vector creates a ‘spike’. The first dose consists of a ‘loaded’ Ad26 vector, and the second dose consists of a ‘loaded’ Ad5 vector. The idea behind using two different viral vectors is to boost immunity and enhance the response of our bodies to the vaccine.
Interval between first and second dose: 21 days
Storage and shelf life
Shelf life: 2 months
Storage:
2 to 8 degree Celsius (dry form)
-18.5 degree Celsius (liquid form)
Efficacy
From data sourced by The Lancet, the efficacy rate of the Sputnik V vaccine after two doses is said to be 91.6 per cent.
Issues developed post-vaccination
No adverse effects were recorded after clinical trials and research. However, common side effects may include symptoms of fever, fatigue, weakness, and headaches.
When will it be available in India?
Sputnik V is the third vaccine registered by India. The Russian Direct Investment Fund (RDIF), which controls the marketing and distribution of the vaccine, plans to produce more than 750 million doses of the vaccine in India. It has partnered with Dr Reddys’ Laboratories to implement the same. Furthermore, the RDIF has collaborated with six domestic vaccine makers to speed up the process. For now, sources say that in India, we will see the availability of the vaccine in May.
Myths and WhatsApp Forwards
Myth: Vaccines can give you COVID.
Fact: The vector injected into the body is essentially a virus, but its gene for mutation is removed. This inserted component is safe for the human body and is recognised by our immune system. Thus, it no longer poses a threat to the body and cannot cause an infection.
Myth: Once vaccinated, you may stop taking precautions against COVID.
Fact: The duration of the immunity offered by vaccines is yet to be studied. There have been quite a few instances of a vaccinated individual contracting COVID, although these instances significantly reduce after administering the second dose. Furthermore, researchers have observed evidence of cases where a vaccinated person has acted as a carrier for the COVID. Vaccination does not ensure that you cannot be infected; mask regulations and social distancing norms should be strictly adhered to post-vaccination.
Myth: The vaccines are unsafe because they’ve been developed quickly.
Fact: The vaccines currently available in India have been researched and developed quickly due to the great effort contributed by scientists to reduce the magnitude and severity of the pandemic. All vaccines have undergone multiple trials and have shown to benefit greatly in providing immunity against COVID. There is an extremely small chance that a person may experience severe side effects due to the vaccine. Apart from this, individuals are monitored for 30 minutes after getting injected in case of any allergic reactions that might occur to the vaccine’s ingredients.
Myth: The vaccines affect female fertility rates and menstrual cycles.
Fact: The vaccine has no effect on fertility rates in women. When it comes to menstrual cycles, there is anecdotal data on women experiencing irregularities in their cycle. However, there isn’t much research on the matter and is not linked with the efficacy rates of the vaccine.
Myth: Women should not take the vaccine five days before or after menstruation.
Fact: A viral WhatsApp forward containing false information is responsible for this myth stating that menstruating women have lower immunity and should avoid taking the vaccine prior to the onset of their cycle. However, the truth is that menstrual cycles and immunity levels have no correlation, and all eligible individuals should sign up for the vaccine regardless of menstrual cycles.
Myth: Pregnant women can’t take the vaccine.
Fact: Pregnant or breastfeeding mothers must discuss their options with their doctor prior to getting vaccinated; this is especially important if they have pre-existing conditions or a high risk of exposure to the virus. However, since the effects of Covaxin have not been studied on pregnant mothers, they should not receive it.
Myth: Individuals who have recovered from Coronavirus do not need to receive the vaccine.
Fact: The duration of the immunity caused by being infected with COVID-19 is not specific, and the chances of getting reinfected vary from person to person. It is recommended that a previously infected individual can get vaccinated after at least fourteen days of asymptomatic recovery. It is important to note that vaccinated individuals cannot donate plasma for up to 28 days from the date of vaccination.
Myth: The Serum Institute of India (SII) is making huge profits by selling vaccines at higher rates in India as compared to other countries.
Fact: Initially, SII and AstraZeneca signed a licencing deal to enable the supply of the vaccine at $3/dose. SII supplied 50 million doses at that price, and another 100 million doses at 66% ($2) of that price to the Indian government. The subsidised prices significantly stressed SII as it still pays around Rs 75 per dose as royalty to AstraZeneca. The current prices of Rs 400/dose align it with parent Astra Zeneca’s price for supplies to the government.
Myth: A higher efficacy rate equals a better vaccine.
Fact: The efficacy of a vaccine is not a guarantee against the chances of infection, rather, it is a measure of the cases that it has reduced in severity. The efficacy rate depends on a lot of factors, like the time and location in which it was tested. Citizens should get vaccinated with any approved vaccine that is assigned to them during registration.
How do I get vaccinated?
Why should everyone get vaccinated?
As of 26th April, the total doses administered in India are as follows:
Total: 14,21,68,770
Dose 1: 11,96,49,166
Dose 2: 2,25,19,604
Vaccines, if allowed to do their job, keep you out of severe illness and death caused by COVID-19. Do your share of research about the vaccines, make sure you aren’t waylaid by myths, and stay well-informed. Take the vaccine at your turn and continue to exercise precaution.
Sources
https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/vaccines/covid-19-vaccine-chadox1-s-recombinant-covishield
https://www.livemint.com/news/india/registration-for-covid-19-vaccines-for-those-above-18-to-start-this-week-how-to-book-appointment-11619075801172.html
https://www.bharatbiotech.com/covaxin.html
https://dashboard.cowin.gov.in/
https://www.instagram.com/p/COH-ZjpqEkM/?igshid=dgvmug5rijf3
Written by Divyansh Kulshreshtha, Pahal Duggal and Suhani Kabra for MTTN
Infographic by Sara Dharmik for MTTN
Featured Image from Daniel Schuldi on Unplash
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.